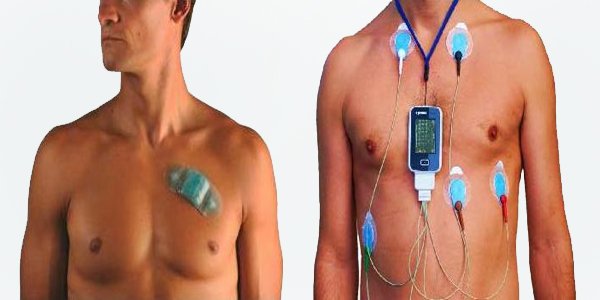
1.Definition and Purpose:
Holter Monitors are portable devices used to continuously record the electrical activity of the heart over 1 to 15Days or longer. They are crucial for diagnosing arrhythmias and other cardiac conditions.
Purpose: To provide a detailed view of heart rhythm over a period of time, capturing irregularities that might not be detected during a standard ECG.
2. Comparison of Wireless and Wired Holter Monitors
A. Technology and Functionality
Wireless Holter Monitors:
Technology: Utilize wireless technology (e.g., Bluetooth or Wi-Fi) to transmit data to a central receiver or cloud-based system.
Functionality: Often feature real-time data transmission, which can be monitored remotely by healthcare providers. May include additional functionalities like mobile app integration.
Wired Holter Monitors:
Technology: Use physical cables and electrodes to record data directly to a portable device.
Functionality: Provide a stable connection with reliable data capture but are restricted by the physical constraints of wires.
B. Patient Comfort and Mobility
Wireless Holter Monitors:
Pros:
Increased Comfort: Fewer wires mean greater comfort and less restriction on movement.
Improved Lifestyle Integration: Allows patients to engage in normal daily activities with less hassle.
Cons:
Potential for Technical Issues: Issues such as signal interference or battery life can affect the monitoring process.
Wired Holter Monitors:
Pros:
Stable Connection: Reliable data transmission without the need for wireless technology.
No Battery Concerns: Operates directly through a power source, eliminating battery life issues.
Cons:
Reduced Comfort: Wires can be cumbersome, limiting patient mobility and comfort.
C. Data Quality and Reliability
Wireless Holter Monitors:
Pros:
Advanced Features: Some models offer real-time monitoring and alerts for irregularities.
Data Management: Can offer cloud-based storage and remote access for healthcare providers.
Cons:
Possible Interference: Wireless signals may be subject to interference, potentially affecting data quality.
Wired Holter Monitors:
Pros:
Consistent Data Quality: Direct connection ensures stable and reliable data capture.
Cons:
Data Management Limitations: Data is usually stored locally and may require manual transfer or retrieval.
D. Patient Experience and Lifestyle Impact
Wireless Holter Monitors:
Pros:
Enhanced Experience: More freedom and less disruption to daily activities, which can lead to a more accurate representation of heart activity.
Cons:
Technological Concerns: Potential issues with technology, such as setup or connectivity problems.
Wired Holter Monitors:
Pros:
Simplicity: Fewer technical issues related to data transmission and fewer concerns about device operation.
Cons:
Physical Limitations: The presence of wires can interfere with normal activities and overall comfort.
E. Cost and Accessibility
Wireless Holter Monitors:
Pros:
Innovative Features: Often come with advanced features that can justify a higher cost.
Cons:
Higher Price: Generally more expensive due to the advanced technology involved.
Wired Holter Monitors:
Pros:
Lower Cost: Typically more affordable and accessible for patients.
Cons:
Fewer Features: May lack some of the modern features found in wireless models.
3. Case Studies and Patient Testimonials
Real-Life Experiences: Blogs often include testimonials from patients who have used both types of monitors, highlighting their personal experiences, challenges, and preferences.
Healthcare Professional Insights: Opinions from cardiologists or medical practitioners on the effectiveness and suitability of each type based on different patient scenarios.
4. Recommendations and Conclusion
Best Use Cases: Blogs often provide guidance on which type of monitor might be better suited for specific needs, such as for patients with active lifestyles or those requiring very precise data monitoring.
Future Trends: Some blogs may discuss emerging technologies and future trends in Holter monitoring, including advancements in wireless technology and innovations in data capture