1. Introduction to Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring
Definition and Purpose:
ABPM involves the continuous measurement of blood pressure over a 24-hour period while the patient goes about their normal daily activities. The primary goal is to obtain a more accurate assessment of blood pressure compared to a single, in-office measurement.
Purpose: To diagnose hypertension, assess the effectiveness of treatment, and evaluate blood pressure variability throughout the day and night.
2. How ABPM Works
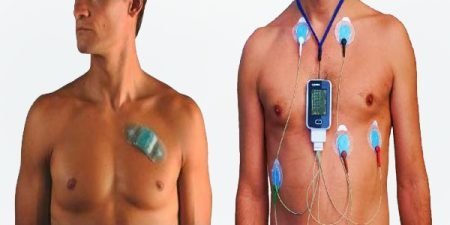
Device Overview:
Equipment: An ABPM device typically consists of a small, portable monitor connected to a cuff that is worn on the upper arm. The monitor records blood pressure readings at regular intervals.
Monitoring Process: The cuff inflates automatically at set intervals (e.g., every 15-30 minutes during the day and every 30-60 minutes at night) to measure blood pressure. The data is stored in the monitor and analyzed later by healthcare professionals.
3. Benefits of ABPM
Accurate Diagnosis:
24-Hour Monitoring: Provides a comprehensive view of blood pressure patterns, including variations during different activities and times of day.
White Coat Syndrome: Helps in distinguishing between true hypertension and elevated readings caused by anxiety during medical visits.
Assessment of Treatment Efficacy:
Medication Monitoring: Evaluates how well blood pressure medications are working over an extended period.
Adjustments: Allows for more informed adjustments to treatment plans based on actual data.
Detection of Nocturnal Hypertension:
Nighttime Readings: Identifies if blood pressure remains high during sleep, which can be an important indicator of health risks.
4. Procedure and What to Expect
Instructions: Patients are usually given instructions on how to prepare for the test, including avoiding caffeine and certain medications.
Fitting the Device: The cuff is placed on the patient’s arm, and the monitor is strapped to their belt or worn on a shoulder strap.
During the Test:
Daily Activities: Patients continue their normal activities while wearing the monitor. They should keep a diary of activities and any symptoms experienced.
Avoiding Interference: Patients are advised to avoid activities that could disrupt the monitoring, such as excessive exercise or getting the device wet.
Post-Test:
Returning the Device: The device is returned to the healthcare provider, who will analyze the recorded data.
Follow-Up: Patients may receive a follow-up appointment to discuss results and any necessary changes to their treatment plan.
5. Interpreting Results
Data Analysis:
Average Readings: Healthcare providers analyze the average blood pressure readings over the 24-hour period, including daytime and nighttime averages.
Patterns: Identification of blood pressure patterns, such as morning surges or nighttime dips.
Clinical Significance:
Diagnosis: Helps in diagnosing various types of hypertension, such as sustained, white coat, or masked hypertension.
Treatment Decisions: Provides a basis for making or adjusting treatment decisions.
6. Patient Experience and Lifestyle Considerations
Comfort and Convenience:
Wearability: While the monitor is designed to be portable, patients might find the cuff and device somewhat cumbersome.
Lifestyle Impact: The need for regular inflations can interrupt daily activities and sleep, but the benefits of detailed data often outweigh these inconveniences.
Common Challenges:
Device Issues: Potential issues with the device, such as discomfort from the cuff or technical malfunctions.
Data Accuracy: Ensuring accurate data collection by following instructions carefully and avoiding activities that could skew results.
7. Cost and Accessibility
Cost Considerations:
Insurance Coverage: Availability and coverage of ABPM may vary depending on insurance plans and healthcare providers.
Out-of-Pocket Costs: Information on potential out-of-pocket expenses for patients without insurance coverage or for those seeking the test privately.
Accessibility:
Availability: ABPM may not be available in all healthcare settings, and access can vary by location and provider.
8. Future Trends and Innovations
Technological Advances:
New Features: Emerging technologies and improvements in ABPM devices, such as smaller, more comfortable cuffs and enhanced data analysis capabilities.
Integration with Digital Health: Potential integration with mobile apps and digital health platforms for more seamless monitoring and data sharing.
Conclusion
Summary: Recap of the benefits and importance of ABPM in providing a comprehensive assessment of blood pressure and improving hypertension management.
Call to Action: Encouragement for readers to discuss ABPM with their healthcare provider if they have concerns about their blood pressure or are seeking a more accurate diagnosis.